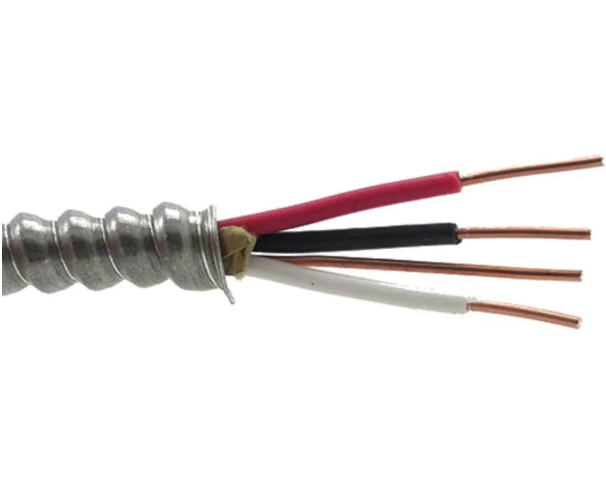
Are you tired of dealing with poor quality core cable that always seem to fail at the worst possible moment? Have you been missing out on important news updates because your current cable just can’t seem to receive a strong signal? If so, it may be time to consider buying good quality core wire.
Core cables help us reducing the hassle of dealing with faulty cables. While there may be some disadvantages to using traditional cables, core cable has the power to address these issues and provide long-lasting solutions. Let’s dive into the world of core cable and how it can positively impact your engineering projects.
What is core cable?
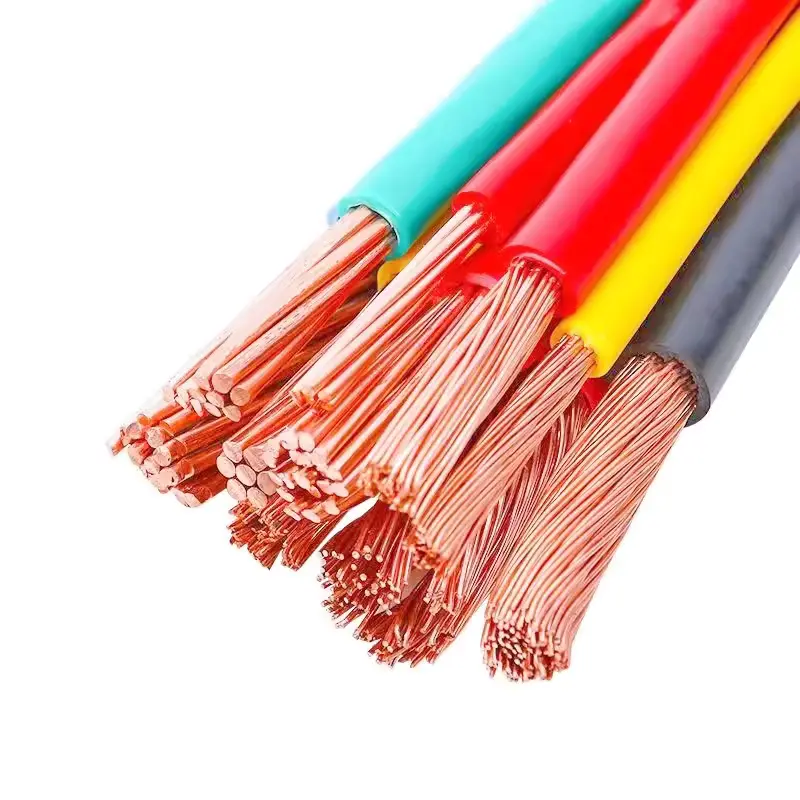

Core cable is a fundamental type of cable that plays a crucial role in transmitting power and signals. It consists of one or more conductors responsible for carrying the electrical current. These conductors are typically made of copper or aluminum, known for their high conductivity and strength. To guarantee safety and efficiency, the outer layer of the core wire is insulated with a material that can vary depending on the application. This insulation serves to protect the conductor from damage and prevent electrical leakage. Core cables are a vital component in a wide range of applications, including power distribution, telecommunications, and electronics
Types of Core Cable
Core cables come in solid, stranded, and braided options. Solid core is best for minimal flexibility and high conductivity, while stranded and braided offer more flexibility and durability. Selecting the type of inner core cable based on the application’s needs is for optimal performance and longevity.
1. Bare Core Cable: This type of core cable is just what it sounds like – bare. It doesn’t have any insulation or protective covering, which can make it more susceptible to damage. However, bare core cables are often used where space is limited or flexibility is required.
2. Insulated Core Cable: Insulated core wire is covered with a layer of insulation, which helps to protect the wires inside from damage. Insulated cable is known for its durability compared to bare core cables, making it a preferred option for use in machine due to its flexibility.
3. Shielded Core Cable: Shielded core cable has an additional layer of shielding around the wires, which helps to reduce electromagnetic interference. This is especially useful when the cables are located near other electronic devices that could cause interference.
4. Twisted Pair Core Cable: Twisted pair core wire consists of two twisted insulated wires. This design helps to reduce crosstalk and interference, making it ideal for applications.
The type of core cable you choose will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Whether you need something flexible, durable, or resistant to interference, a core wire solution exists for you. Just make sure to consider all the factors before making a decision.
Single Core Cable Vs. Multi Core Cable: How to choose?
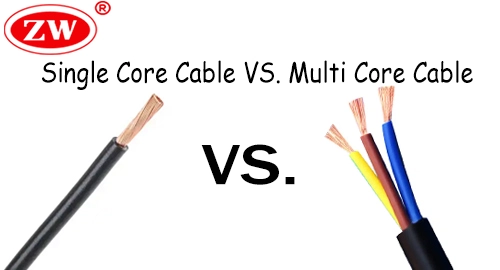
When deciding whether to use a single-core cable or a multi-core cable, it’s important to consider several factors. A single-core cable has one solid conductor, while a multi-core cable has multiple conductors bundled together. The decision to use a single-core or multi-core cable depends on the project’s specific requirements for flexibility, ease of installation, and signal transmission.
A multi-core cable could be an excellent option if you’re searching for a cable that can transmit multiple signals simultaneously. They are typically used in low voltage control systems or in communication systems.Due to its convenient and versatile installation, multi-core cable is suitable for a variety of applications. On the other hand, a single-core cable is more straightforward and sufficient for simpler applications. A single-core cable can be used in high voltage. It’s important to carefully assess your requirements and consult a professional to determine which type of cable suits your needs.
The decision between a single-core cable and a multi-core cable ultimately depends on the specific demands of your project, which will be determined by factors such as flexibility, ease of installation, and signal transmission requirements.
Read More:Single Core Cable VS Multi-Core: What’s The Differences?
core cable vs pair cable
Core cables and pair cables are two distinct types of electrical cables. Understanding the differences between these two types is essential for selecting the appropriate cable for a given application.
Core cables are electrical cables that consist of a single conductor at their core, surrounded by insulation material such as PVC or XLPE. They are commonly used for power transmission or signal transmission applications and can handle low to high voltage levels. The simplicity of their design makes them ideal for use in a wide range of settings, from residential wiring to industrial power distribution. Core cables are known for their ability to provide a single path for electrical current, making them suitable for applications that require a straightforward approach.
Pair Cables are made up of two insulated wires that are twisted together. This unique configuration provides structural integrity and plays a vital role in minimizing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI). The twisting helps cancel out noise that may interfere with the signals that travel through the wires, making Pair Cables an ideal choice for telecommunications, data transmission, and applications where signal integrity is paramount. The twisted design of cables reduces interference and makes them less vulnerable to external noise sources, resulting in more effective communication channels in environments prone to electrical noise.

Advantages and disadvantages of Core Cable
Core cables are widely used in electrical and electronic systems due to their high performance and durability. However, when planning and designing systems, it’s important to consider both the benefits and drawbacks of using core cables. Let’s explore the technical details of these pros and cons.
Advantages
- Efficiency in Power Transmission: Core cables are excellent for power transmission over extended distances due to their high efficiency. Their single-conductor design helps minimize power loss, making them for high-voltage power transmission applications that maintain efficiency over long distances.
- Simplicity in Design: Core cables are simpler than multi-conductor cables, with only one conductor encased in insulation. This simplicity facilitates easier installation and maintenance, reducing overall system complexity.
- Durability and Longevity: The conductors of the core wire are protected by an insulating layer that provides excellent durability. They can withstand environmental stresses and mechanical wear over time, leading to a longer lifespan.
- High Current Carrying Capacity: Single-core cables have a higher current carrying capacity than multi-core cables of the same cross-sectional area. The higher current carrying capacity in multi-stranded conductors is due to the reduced risk of heat accumulation, leading to more efficient current flow. Because the heat generated within a single conductor is not concentrated in one area, allowing for better heat dissipation and less resistance to current flow.
Disadvantages
- Limited Flexibility: Core cables, especially those with larger diameters, tend to be less flexible. The inflexibility of cables can pose a challenge while installing them in confined spaces or where they need to be frequently bent.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Single-core cables can be more susceptible to electromagnetic interference since they lack the shielding in some multi-conductor cables. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can significantly impact the quality of signals in applications that are sensitive to it.
- Thermal Limitations: While core cables can handle high currents, they also have thermal limitations. If the current exceeds a certain threshold, there is a risk of overheating, which can damage the cable and surrounding equipment.
- Application Restrictions: Due to their design, core cables are only suitable for some applications. They are primarily used for power transmission and may not be ideal for tasks requiring multiple signals simultaneously, where multi-core or paired cables would be more appropriate.
Core Cable Conclusion
Core cable is essential for guaranteeing smooth and efficient electrical connections in various applications. Understanding the factors contributing to core cables’ quality and performance is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
When considering purchasing wire and cable manufacturer, ZW Cable is the go-to choice due to its extensive range of high-quality products and strict requirements for cable quality. By choosing your best electrical wire cable, you can be confident that you are getting the best value for your money. Most of cables are in available in stock.
Upgrade your electrical systems by purchasing electric core cable from ZW Cable today. This investment will pay off in terms of better quality and performance for future projects. Contact us we will offer your best price.
FAQS:
What is a core in a cable?
what is 5 core cable used for?
A 5-core cable is a conductor cable that can carry multiple circuits and signals simultaneously while providing additional conductors for control and monitoring functions. Five conductors cable is particularly beneficial for intricate applications such as cable machines, lighting, control panels, and emergency systems.
2 c0re cable vs 3 core cable: what is the difference
The primary difference between a 2-core cable and a 3-core cable lies in the number of insulated conductors, or “cores,” each contains, which directly affects their applications and functionality:
- 2-Core Cable: This cable type has two insulated conductors and is a versatile option. It is commonly used for simple electrical applications that require just two paths for the current to flow, such as live and neutral wires in basic lighting circuits or in power supply for single-phase appliances. The absence of a dedicated ground wire makes 2-core cables ideal for situations where grounding can be accomplished through other means or in double-insulated appliances that do not require grounding.
3-Core Cable: A 3-core cable offers a significant safety advantage with its three insulated conductors, including a dedicated ground (earth) wire alongside the live and neutral wires in many electrical installations. It provides a safe path for fault current to dissipate into the earth in the event of a short circuit or other fault condition. This safety feature is why 3-core cables are widely used in applications that require a grounded connection to enhance user safety and comply with electrical codes, such as in building wiring, outdoor lighting, and appliances where additional grounding is necessary.